December 13, 2024
How Many Eggs Does a Woman Have? Reasons Behind Quality & Quantity Decline
Exploring the biological reasons behind declining egg quality and quantity and how freezing preserves younger eggs.

Maggie Jones
Registered Nurse
10 Minute Read
The fertility journey can often feel a little overwhelming, especially when faced with concerns about egg quantity and quality. How many eggs does a woman typically have, and does their quality decline over time? More importantly, how do these factors affect your chances of conception?
Elsa Fertility is here to help you understand the biological reasons behind declining egg quality, as well as the role of egg freezing in preserving your eggs. With this knowledge, you’ll feel more confident making decisions about your reproductive health.
How Many Eggs Does a Woman Have at Different Life Stages?
Individuals with ovaries are born with all of the eggs they will ever have—once they're gone, they can’t generate new ones.
So, how many eggs do you have? At birth, your ovaries carry about 2 million eggs, but as a part of the normal aging process, this number diminishes by approximately 1,000 eggs each month. On average, this is what your ovarian reserve looks like at various life stages:
Puberty: Around 300,000 eggs
20s: 150,000 to 300,000 eggs
Early 30s: 100,000 to 150,000 eggs
Late 30s: Around 27,000 eggs
Late 40s: 5,000 to 10,000 eggs
Menopause: Less than 1,000 eggs
The rate of decline tends to speed up once you reach your mid-30s. For some individuals, the rate of decline is even faster, though the reasons for this are often unknown.
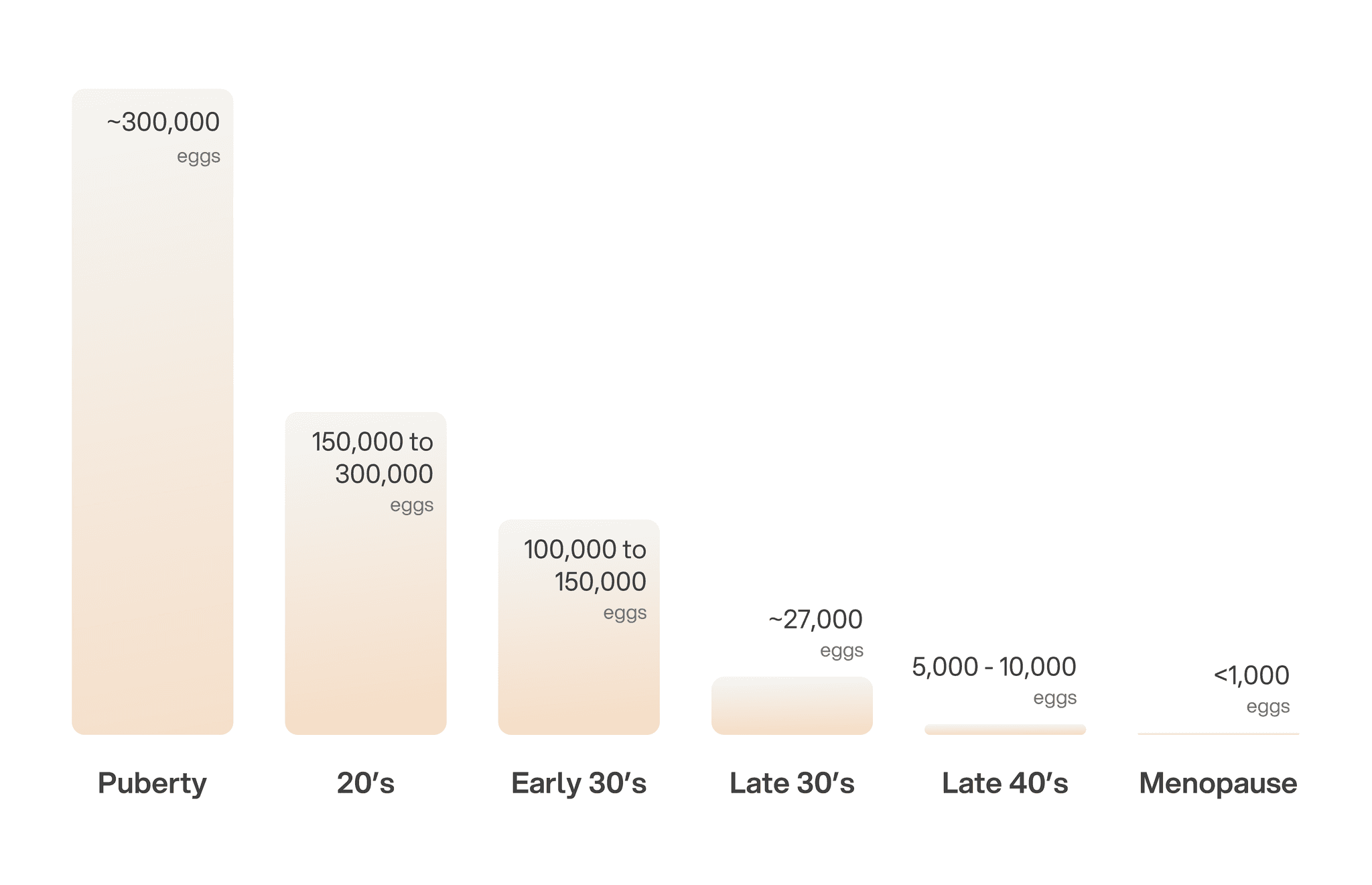
What Happens During Ovulation—and Why Do Eggs Decline?
Ovulation is the monthly process where your ovaries release one mature egg, giving you a chance to conceive. But it’s not just that one mature egg that’s lost each month.
Before ovulation, a group of follicles, each containing an immature egg, begins to develop. Only one egg matures and is released, while the others break down and are reabsorbed by the body. This is why your egg count declines even when you’re not actively trying to conceive.
Over time, the pool of available eggs—called your ovarian reserve—shrinks.
Egg Quality vs. Quantity: Why Both Matter for Fertility
Egg quantity is not the only factor at play. Fertility depends on two key factors: quantity (the number of eggs in your ovaries) and quality (how healthy those eggs are). Egg quality refers to whether an egg has the correct number of chromosomes—23 to be exact—which makes them more likely to fertilize.
As egg quantity decreases with age, so does quality. Older eggs are at a higher risk of genetic or chromosomal imbalances, leading to issues like infertility, miscarriage, or genetic conditions such as Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21). While it only takes one healthy egg to get pregnant, the odds of finding that egg decrease as time goes on.
Other Factors Contributing to Egg Quality and Quantity Decline
While the natural decline of the ovarian reserve plays a significant role, several other factors also contribute to this process.
Medical Conditions
Chronic illnesses and autoimmune disorders, which can impact fertility. For instance, Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID), which can cause scarring in the fallopian tubes, is known to lead to infertility in approximately 1 in 10 women. Treatments like chemotherapy and radiation can also reduce the quantity and quality of eggs.
Lifestyle Choices
Your habits also play a role in your fertility health. Smoking, for example, speeds up egg loss and increases the risk of issues with the eggs' DNA, while excessive drinking of alcohol can be disruptive to your hormone levels and fertility.
While a proper lifestyle won't stop the natural decline in egg quantity, it can reassure you that the eggs you do have are as healthy as possible. Maintaining a poor diet and being subjected to chronic stress may impair your ovarian function and cause difficulties with producing hormones.
How Egg Freezing Helps Protect Your Fertility
Poor egg quality can lead to a higher risk of miscarriage and complications during pregnancy, such as developmental issues or genetic disorders. This decline in egg quality can also make it difficult to get pregnant, as eggs may not fertilize as easily or may not implant properly in the uterus.
This is where fertility preservation options can help. Freezing eggs allows you to preserve your eggs while they’re viable—by doing so, you can give yourself the best chances of conception when you’re ready, even if it’s still years in the future. Here are some of the benefits of egg freezing:
Quality Preservation
Freezing eggs maintains their quality—or genetic potential—based on the age at the time of freezing. This increases the chances of successful fertilization and healthy pregnancies later on in life.
Flexibility and Control
Fertility egg preservation lets you focus on personal, professional, or health-related goals without the immediate pressure to conceive. That way, you can plan for the future while taking control of your reproductive health.
Improved Pregnancy Outcomes
Preserving high-quality eggs for the future can reduce the risk of implantation failure, miscarriage, and pregnancy complications like birth defects.
How Does Egg Freezing Work?
While declining egg quality and quantity are a natural part of aging, egg freezing offers a proactive option for those looking to preserve their fertility. Egg freezing (or oocyte cryopreservation) is a process designed to preserve eggs for future use.
Here’s what to expect from this fertility egg preservation method:
Ovarian Stimulation: Stimulating the ovaries promotes the growth of multiple follicles, each containing an egg. This process typically lasts 10 to 14 days.
Egg Retrieval: Once the follicles reach a certain size, and are hormonally active based on ultrasound and blood testing, they are retrieved through a minor surgical procedure. An ultrasound is used to guide a small needle through the vagina and into the ovaries. The needle is then used to collect the fluid from each follicle, which contains the eggs.
Freezing: The mature eggs are then frozen via a process called vitrification. This involves rapidly cooling the eggs to prevent ice crystals from forming, which could damage them and affect their viability.
When should you consider freezing your eggs? The ideal time is typically in your late 20s to early 30s when egg quality is at its peak. Freezing your eggs while you’re young can offer you the best chances of conception in the future.
To understand the best course of action based on your circumstances, consult with a reproductive health professional near you. At Elsa, we simplify the process by connecting you with licensed reproductive experts in your area, ensuring a seamless and stress-free experience.
Take the First Step Toward Fertility Preservation with Elsa
The fertility journey can be challenging to navigate, especially when considering the natural decline in egg quality and quantity over time. If you're concerned about your fertility or want to preserve your options for the future, egg freezing can empower you to take control of your reproductive health.
Get in touch with Elsa today. With the right support, you can make decisions that align with your goals, and have the best possible chance for family-building in the future.
© 2024 Elsa Fertility. All rights reserved.






